Extracellular transglutaminase-2 in tissue fibrosis: a new therapeutic avenue
TG2 has been implicated in the pathogenesis of many apparently unrelated diseases such as tissue fibrosis, celiac disease, cancers, neurodegenerative disorders, and type-2 diabetes. Although capable of different biological activities, overall its expression and activation is believed to occur as a response to tissue injury and / or cell stress. Protein cross-linking is the enzymatic reaction for which TG2 is better known, involving an acyl transfer reaction between the gamma carboxamide group of a peptide-bound Gln residue and the epsilon-amino group of a peptide-bound Lys residue or a primary amino group of a polyamine. TG2 causes additional post-translational modifications among which protein deamidation of Gln residues contributes to the development of disorders caused by gluten sensitivity. A recent review from our lab: Savoca et al 2018
What have we achieved?
- Identification of a novel pathway mediated by TG2 via MUC1, contributing to androgen insensitivity and malignancy in prostate cancer Silencing of TG2 by CRISPR-Cas9 is associated with upregulation of androgen receptor transcription in PCa cell lines and a reduced level of mucin-1 (MUC1), which was restored by selective add-back of the truncated TG2 isoform (TGM2_v2). TG2 affects transcriptional regulation of MUC1 via repressing AR expression (Atobatele 2023)
Mapping of the TG2 interactome in chronic kidney disease (CKD). A differential proteomic approach was developed to identify disease gene-associated proteins in kidney membrane, with support from Kidney Research UK (study published in Furini et al 2018)
Identification of the role of Syndecan-4 in the biological activity of extracellular TG2 in fibrosis. The partnership of TG2 and Syndecan-4 was elucidated in experimental models of kidney fibrosis (unilateral ureteric obstruction (UUO) and aristolochic acid nephropathy (AAN)) in vivo (Scarpellini et al 2014) and ex vivo (Burhan et al 2016)
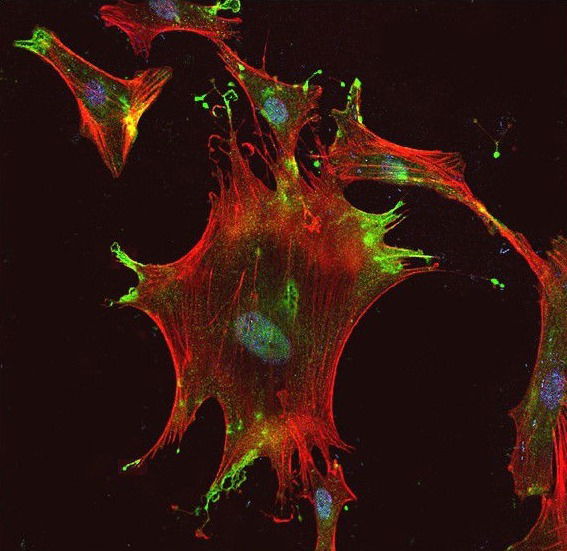
Characterisation of the heparin binding property of TG2. The affinity binding of TG2 for heparan sulphate (HS) was demonstrated biochemically by solid binding assays and co-immunoprecipitation, and by double immunofluorescent staining of fixed and stained primary cells. The significance of the syndecan-4/HS-TG2 association in TG2 cell surface trafficking/localisation was investigated in primary cell models Scarpellini et al 2029; Lortat-Jacob&Burhan 2012; Furini 2019
Identification of a TG2-fibronectin mediated cell survival pathway. A matrix TG2-mediated cell survival pathway independent of the Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD)-main cell adhesion site of fibronectin was reported with relevance in matrix fragmentation / tissue injury Telci 2008; Verderio 2003